IPFS 프로토콜 라우팅 계층 분석
IPFS 프로토콜 계층 심층 분석
IPFS는 아키텍처를 6 개의 레이어로 추상화합니다. 각 레이어는 기술 구현 또는 특정 기술 솔루션을 가지고 있습니다. 프로토콜로서 IPFS는 인터페이스 형태로 레이어 간의 기능 및 상호 호출 관계를 정의합니다.

라우팅 계층 프로토콜
두 번째 레이어인 라우팅 레이어부터 시작하고자 하는데, 디자인의 첫 번째 레이어인 네트워크 레이어는 기본적인 네트워크 장비 또는 네트워크 기능으로 이해할 수 있습니다. 또한 암호화 전송, 다중 링크 혼합 및 기타 기술을 추가하는 지점 간 링크를 구축 할 수 있습니다. 다음 그림은 IPFS 스택에 대한 기반 기술을 표현한 그림입니다.
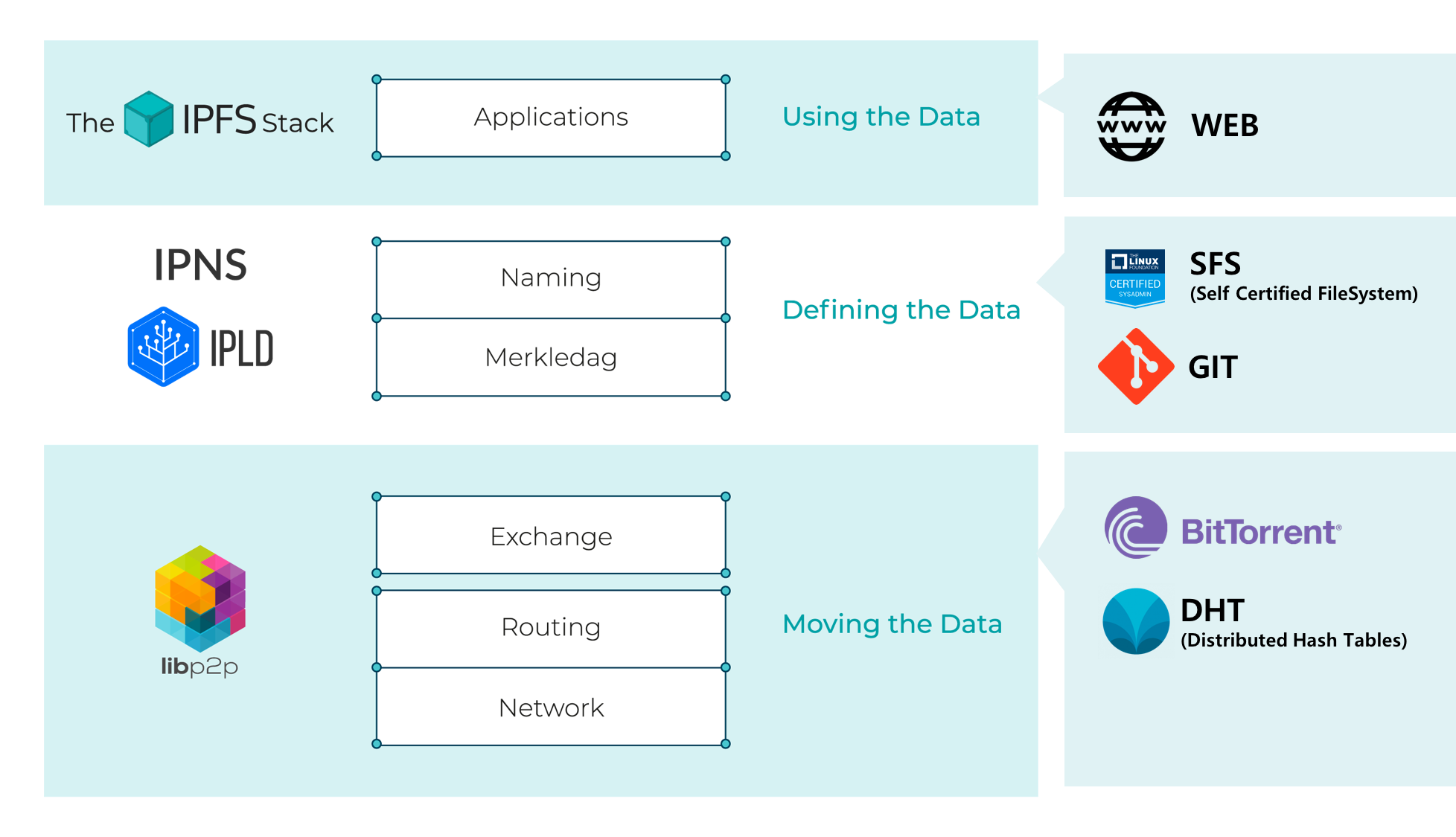
IPFS 라우팅
라우팅 레이어가 인터페이스 형태로 제공하는 기능을 정의합니다. 라우팅 레이어는 저장된 콘텐츠 검색 및 IPFS 노드의 경로 조회를 지원합니다. 이를 위해 DHTS, mdns, snr 또는 DNS 프로토콜을 사용할 수 있습니다. 네트워크에서 라우팅 프로토콜의 구성은 노드 및 라우팅 데이터를 찾은 다음 init으로 실행되는 IPFS 초기화를 실행합니다. local-discovery를 통하여, IPFS 시스템은 mdns를 라우팅 계층을 로드합니다.
라우팅 레이어 프로토콜의 함수 정의입니다. 다음과 같이 인터페이스 형식으로 표현합니다.
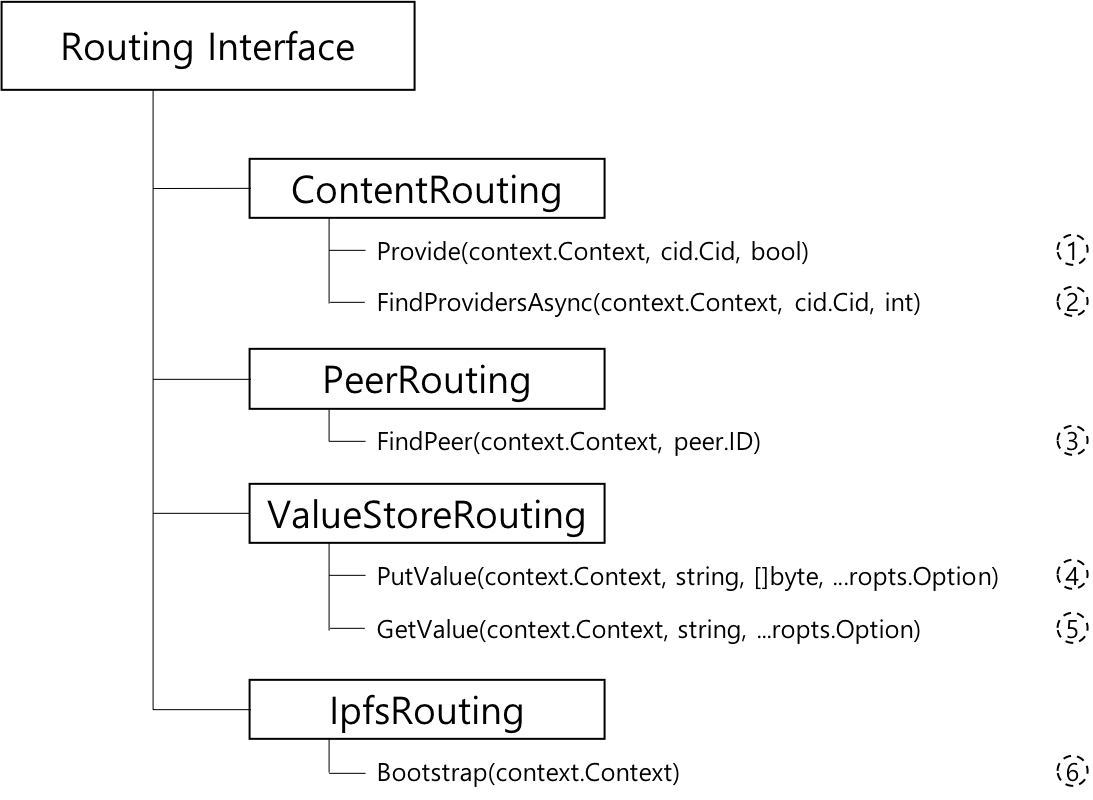
위 그림은 IPFS 라우팅 계층 프로토콜이 가져야하는 기본 기능을 나타냅니다.
- ContentRouting: ContentRouting은 간접적인 가치 제공자 계층으로 누가 어떤 컨텐츠를 가지고 있는지에 대한 정보를 찾는 데 사용됩니다.
Provide: 특정 키에 따라 현재 노드가 키에 해당하는 값의 저장 위치를 찾고 필요한 경우 브로드캐스트 방식으로 가장 가까운 IPFS 노드에 정보를 브로드캐스팅 할지 여부를 결정합니다. 자신의 IPFS 노드는 키에 해당하는 내용의 저장 경로를 기록하고 상황에 따라 다른 노드에 브로드캐스트하여 다른 사람에게이 노드가 키에 대한 라우팅 정보를 알고 있음을 알립니다.FindProvidersAsync: 키의 라우팅 정보를 알고있는 노드 정보를 획득 할 수 있는 노드의 최대 수를 제한 할 수 있습니다.
- PeerRouting: PeerRouting은 은 특정 피어에 대한 정보를 찾는 방법입니다. 이것은 간단한 룩업 테이블, 트래킹 서버 또는 DHT를 통해 구현될 수 있습니다.
FindPeer: 노드의 ID에 따라 노드에 대한 네트워크 서비스 정보를 얻을 수 있습니다. 키는 IPFS 노드의 ID를 나타내고 반환 정보는 노드에 대한 네트워크 계층 데이터 (예: 포트 번호 및 서비스를 제공하기 위한 프로토콜 유형) 입니다.
- ValueStore: ValueStore는 기본 Put/Get 인터페이스입니다.
PutValue: 라우팅 레이어가 키의 저장 경로뿐만 아니라 키에 대한 특정 콘텐츠를 캐시 할 수 있으며 키에 가장 가까운 라우팅 노드에 콘텐츠를 브로드캐스트 합니다. 정보를 받은 후, 다른 라우팅 테이블은 자신의 라우팅 테이블에 정보를 저장해야 합니다.GetValue: 주어진 키에 따라 라우팅 테이블에 직접 저장된 키에 해당하는 콘텐츠를 얻습니다.
- IpfsRouting: IpfsRouting은 ipfs가 사용하는 서로 다른 라우팅 유형의 조합입니다. 단일 항목(예: DHT) 또는 각 작업에 더 최적화된 여러 개의 다른 부분으로 만족될 수 있습니다.
Bootstrap: 주기적으로 라우팅 테이블 정보를 업데이트하는 타이밍 기능입니다. 분산 라우팅 프로토콜이기 때문에 라우팅 테이블 타이밍에 따라 노드의 업 링크 및 오프라인 정보를 동기화하고 업데이트해야 합니다. Bootstrap 을 통해 호출자는 라우팅 시스템에 힌트를 표시하여 Boostrapped 상태가됩니다.
IPFS의 라우팅 관련 내용은 다음에서 확인가능 합니다.
- go-ipfs-routing
go-ipfs-routing은go-ipfs에 사용되는go-libp2p-routing구현
- go-libp2p-routing
아래는 IPFS에서 사용되는 go-libp2p 패키지중 go-libp2p-routing/routing.go 코드의 일부입니다.
// package routing defines the interface for a routing system used by ipfs.
package routing
import ...
// ErrNotFound is returned when the router fails to find the requested record.
var ErrNotFound = errors.New("routing: not found")
// ErrNotSupported is returned when the router does not support the given record
// type/operation.
var ErrNotSupported = errors.New("routing: operation or key not supported")
// ContentRouting is a value provider layer of indirection. It is used to find
// information about who has what content.
type ContentRouting interface {
// Provide adds the given cid to the content routing system. If 'true' is
// passed, it also announces it, otherwise it is just kept in the local
// accounting of which objects are being provided.
Provide(context.Context, cid.Cid, bool) error
// Search for peers who are able to provide a given key
FindProvidersAsync(context.Context, cid.Cid, int) <-chan pstore.PeerInfo
}
// PeerRouting is a way to find information about certain peers.
// This can be implemented by a simple lookup table, a tracking server,
// or even a DHT.
type PeerRouting interface {
// Find specific Peer
// FindPeer searches for a peer with given ID, returns a pstore.PeerInfo
// with relevant addresses.
FindPeer(context.Context, peer.ID) (pstore.PeerInfo, error)
}
// ValueStore is a basic Put/Get interface.
type ValueStore interface {
// PutValue adds value corresponding to given Key.
PutValue(context.Context, string, []byte, ...ropts.Option) error
// GetValue searches for the value corresponding to given Key.
GetValue(context.Context, string, ...ropts.Option) ([]byte, error)
// TODO
// SearchValue searches for better and better values from this value
// store corresponding to the given Key. Implementations may halt the
// search after a period of time or may continue searching indefinitely.
//
// Useful when you want a result *now* but still want to hear about
// better/newer results.
//SearchValue(context.Context, string, ...ropts.Option) (<-chan []byte, error)
}
// IpfsRouting is the combination of different routing types that ipfs
// uses. It can be satisfied by a single item (such as a DHT) or multiple
// different pieces that are more optimized to each task.
type IpfsRouting interface {
ContentRouting
PeerRouting
ValueStore
// Bootstrap allows callers to hint to the routing system to get into a
// Boostrapped state
Bootstrap(context.Context) error
// TODO expose io.Closer or plain-old Close error
}
...
